Diagnostics
Neurological symptoms require precise diagnostics to identify their cause effectively.
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS/ENG)
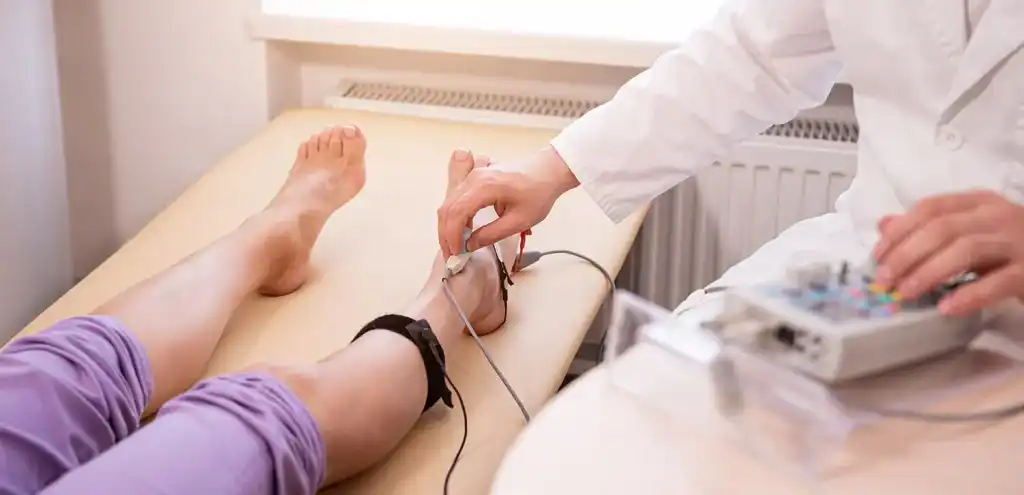
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS/ENG)
Electroneurography is an electrical measurement used to evaluate nerve function. By stimulating a nerve with small electrical impulses, the response and transmission speed of the signal can be measured. This allows determination of the nerve conduction velocity (NCV). A reduced speed or intensity may indicate conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome or polyneuropathy. Adhesive electrodes are placed on the skin of the hands or feet. You will be seated or lying comfortably during the approx. 10-minute exam, which is generally well tolerated and not painful.
Electromyography (EMG)
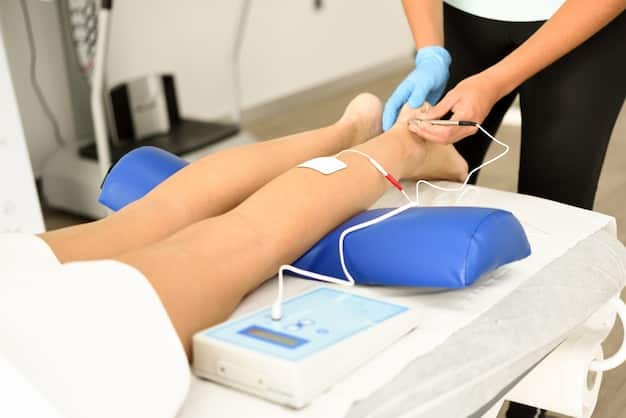
Electromyography (EMG)
This test evaluates muscle activity and is used in suspected muscle diseases or to check if a herniated disc is pressing on a nerve. A sterile, fine needle is inserted into muscles in the arms or legs. The test is performed at rest, during light contraction, and stronger muscle effort. Muscle activity is recorded audibly, so you can “hear” your muscles working. You lie comfortably on a table; the exam lasts approximately 20 minutes.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
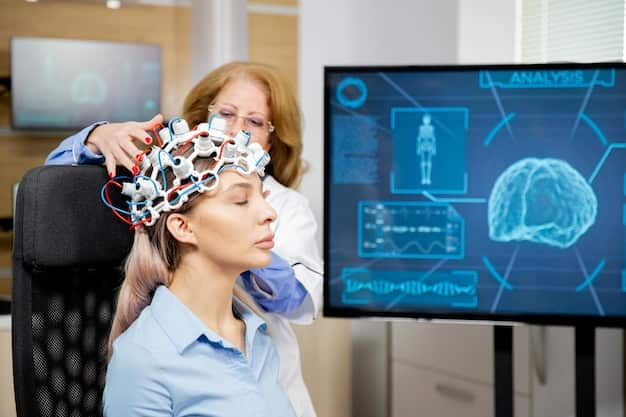
Electroencephalography (EEG)
EEG is a key tool in diagnosing epilepsy and dementia. Surface electrodes are placed on the scalp using a flexible cap, and brain waves are measured. You sit comfortably and follow simple instructions. The exam takes about 30 minutes.
Evoked Potentials (EP)
Evoked Potentials (EP)
Evoked potentials test the conductivity and function of nerve pathways. A sensory stimulus triggers brain activity, which is analyzed to identify abnormalities. Types include:
VEP – Visual Evoked Potentials
AEP – Auditory Evoked Potentials
SEP – Somatosensory Evoked Potentials
MEP – Motor Evoked Potentials
Visual Evoked Potentials (VEP)

Visual Evoked Potentials (VEP)
VEP measures the signal speed along the optic nerve to the visual cortex. You’ll look at a checkerboard screen and focus on a red dot while one eye is covered. You sit comfortably. This 20-minute test helps diagnose visual pathway disorders
Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SEP)
Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SEP)
This test assesses nerves responsible for touch and pressure sensations in the arms, legs, or face. It uses adhesive electrodes and mild electrical impulses to examine sensory pathways from limbs through the spinal cord to the brain. You lie comfortably, and the test lasts about 20 minutes.
Auditory Evoked Potentials (AEP)

Auditory Evoked Potentials (AEP)
AEP evaluates the auditory pathways from the ears to the brain and can be useful in diagnosing balance disorders. You wear headphones and hear clicking sounds while electrodes behind the ears record responses. Both sides are tested separately. The procedure takes about 20 minutes.
Memory Testing

Memory Testing
If dementia is suspected, standardized tests assess various memory functions.
Botulinum Toxin Injections
Botulinum Toxin Injections
Botulinum toxin is used in neurology to treat spasticity, chronic migraine, and excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis). Precisely injected, it suppresses overactive nerve signals—bringing relief and improved quality of life.
The injection is performed with a fine needle and is generally well tolerated—similar to a vaccination. The session lasts 15–30 minutes depending on the region treated. Anesthesia is usually not required.
Ultrasound of the Neck Vessels
Ultrasound of the Neck Vessels
This non-invasive, radiation-free procedure takes about 20 minutes while you lie comfortably. Gel is applied, and a transducer is moved over the carotid artery area.
We assess the vessel walls (intima-media complex) and blood flow in the common, external, and internal carotid arteries as well as the vertebral artery. The Doppler method allows detection and measurement of narrowings or expansions (atherosclerosis).